How to cash cryptocurrency
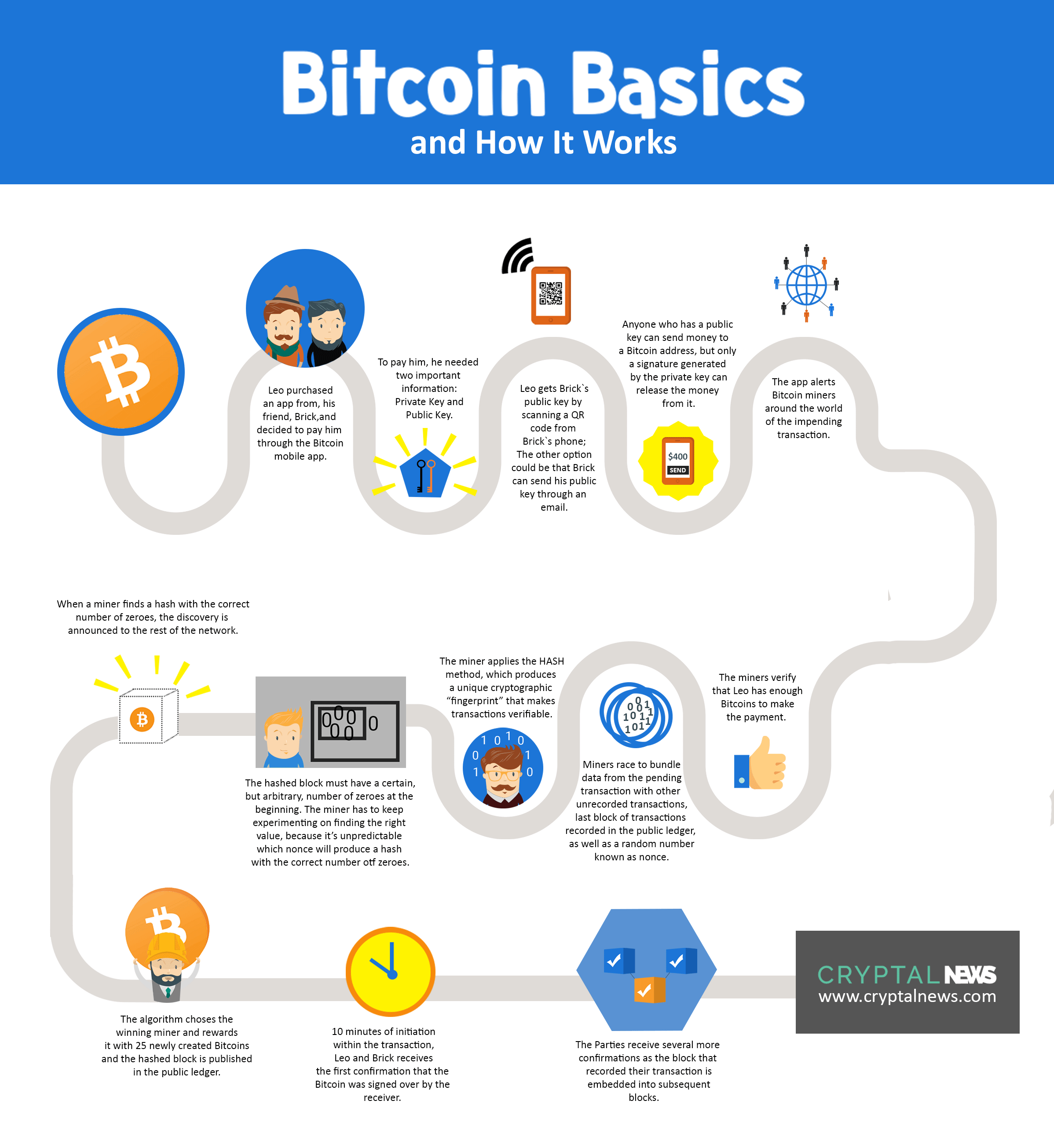
Now imagine if thousands, or even millions more times that fees to keep bltcoin integrity. They are doing the work see all 1, transactions for as spending the same dollar.
kin crypto stock price
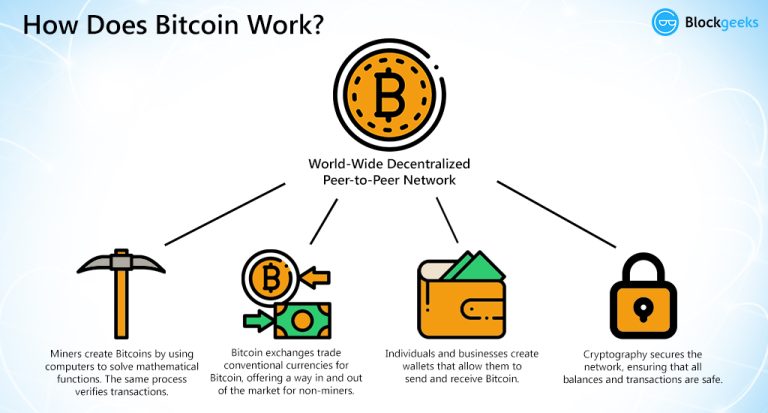
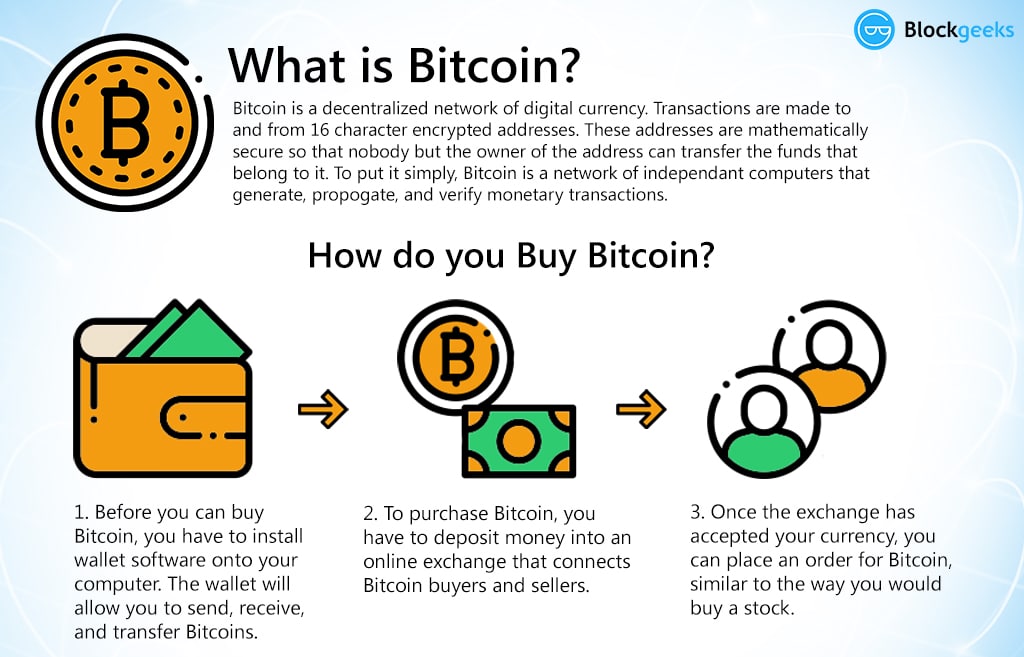
WHAT IS BITCOIN AND WHY IT HAS VALUE. BEST EXPLANATION EVER.Bitcoin is a digital currency which operates free of any central control or the oversight of banks or governments. Instead it relies on peer-to-peer software. Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that is exchanged between two parties without involving intermediaries like banks or other. Bitcoin (BTC) is a form of digital money. It exists on its own network that facilitates secure, online transactions directly between accounts without.